Have you caught cryptocurrency fever, or are you at least wondering what it’s all about? Odds are, you hadn’t even heard the term until recently. Now, it seems as if everybody and their cousin are getting in on it.
Psychologists have assigned a term to the angst you might be feeling in the heat of the moment. It’s called “FoMO” or Fear of Missing Out. Education is the best first step toward facing FoMO and making informed financial choices that are right for you. So before you make any leaps, let’s take a closer look.
What is cryptocurrency?
Crytpocurrency is essentially a kind of money – or currency. Thanks to electronic security – or encryption – it exists in a presumably secure, sound and limited supply. Pair the “encryption” with the “currency,” and you’ve got a new kind of digital asset, or electronic exchange.
Well, sort of new. Cryptocurrency was introduced in 2009, supposedly by a fellow named Satoshi Nakamoto. His Wikipedia entry suggests he may not actually be who he says he is, but minor mysteries aside, he (or possibly “they”) is credited with designing and implementing
bitcoin as the first and most familiar cryptocurrency. Ethereum is currently its second-closest competitor, with plenty of others vying for space as well (more than 1,300 as of early December 2017), and plenty more likely to come.
Unlike a dollar bill or your pocket change, cryptocurrency exists strictly as computer code. You can’t touch it or feel it. You can’t flip it, heads or tails. But increasingly, holders are receiving, saving and spending their cryptocurrency in ways that emulate the things you can do with “regular” money.
How does cryptocurrency differ from “regular” money?
In comparing cryptocurrency to regulated fiat currency – or most countries’ legal tender – there are a few observations of note.
First, since neither fiat nor cryptocurrency are still directly connected to the value of an underlying commodity like gold or silver, both must have another way to maintain their spending power in the face of inflation.
For legal tender, most countries’ central banks keep their currency’s spending power relatively stable. For cryptocurrency, there is no central bank, or any other centralized repository or regulator. Its stability is essentially backed by the strength of its underlying ledger, or blockchain, where balances and transactions are verified and then publicly reported.
The notion of limited supply factors in as well. Obviously, if everyone had an endless supply of money, it would cease to have any value to anyone. That’s why central banks (such as the U.S. Federal Reserve, the Bank of Canada, and the Bank of England) are in charge of stabilizing the value of their nation’s legal tender, regularly seeking to limit supply without strangling demand.
While cryptocurrency fans offer explanations for how its supply and demand will be managed, it’s not yet known how effective the processes will be in sustaining this delicate balance, especially when exuberance- or panic-driven runs might outpace otherwise orderly procedures. (If you’re technically inclined and you’d like to take a deep dive into how the financial technology operates, here’s one source to start with.)
Why would anyone want to use cryptocurrency instead of legal tender?
For anyone who may not be a big fan of government oversight, the processes are essentially driven “by and for the people” as direct peer-to-peer exchanges with no central authorities in charge. At least in theory, this is supposed to allow the currency to flow more freely, with less regulation, restriction, taxation, fee extraction, limitations and similar machinations. Moreover, cryptocurrency transactions are anonymous.
If the world were filled with only good, honest people, cryptocurrency and its related technologies could represent a better, more “boundary-less” system for more freely doing business with one another, with fewer of the hassles associated with international commerce.
Unfortunately, in real life, this sort of unchecked exchange can also be used for all sorts of mischief – like dodging taxes, laundering money or funding terrorism, to name a few.
In short, cryptocurrency, blockchain technology, and/or their next-generations could evolve into universal tools with far wider application. Indeed, such explorations already are under way. In December 2017, Vanguard announced collaborative efforts to harness blockchain technology for improved index data sharing.
That said, many equally promising prospects have ended up discarded in the dustbin of interesting ideas that might have been. Time will tell which of the many possibilities that might happen actually do.
Even if I don’t plan to use cryptocurrency, should I hold some as an investment?
If you do jump in at this time, know you are more likely speculating than investing.
Bubble or not, consider these two points. First, there are a lot of risks inherent to the cryptocurrency craze. Second, cryptocurrency simply doesn’t fit into our principles of evidence-based investing … at least not yet.
Let’s take a look at the risks.
Regulatory Risks – First, there’s the very real possibility that governments may decide to pile mountains of regulatory road blocks in front of this currently free-wheeling freight train. Some countries have already banned cryptocurrency. Others may require extra reporting or onerous taxes. These and other regulations could severely impact the liquidity and value of your coinage.
Security Risks – There’s also the ever-present threat of being pickpocketed by cyberthieves. It’s already happened several times, with millions of dollars of value swiped into thin air. Granted, the same thing can happen to your legal tender, but there is typically far more government protection and insurance coverage in place for your regulated accounts.
Technological Risks – As we touched on above, a system that was working pretty well in its development days has been facing some serious scaling challenges. As demand races ahead of supply, the human, technical and electric capital required to keep everything humming along is under stress. One recent post estimated that if bitcoin technology alone continues to grow apace, by February 2020, it will suck away more electricity than the entire world uses today.
That’s a lot of potential buzzkill for your happily-ever-after bitcoin holdings, and one reason you might want to think twice before you pile your life’s savings into them.
Then again, every investment carries some risk. If there were no risk, there’d be no expected return. That’s why we also need to address what evidence-based investing looks like. It begins with how investors (versus speculators) evaluate the markets.
What’s a bitcoin worth? A dollar? $100? $100,000? The answer to that has been one of the most volatile bouncing balls the market has seen since tulip mania in the 1600s.
In his ETF.com column “Bitcoin & Its Risks,” financial author Larry Swedroe summarizes how market valuations occur. “With stocks,” he says, “we can look at valuation metrics, like earnings yield. With bonds, we can use the current yield-to-maturity. And with assets like reinsurance or lending … we have historical evidence to make the appropriate estimates.”
You can’t do any of these things with cryptocurrency. Swedroe explains: “There simply is no tangible relationship between any economic or financial parameters and bitcoin prices.” Instead, there are several ways buying cryptocurrency differs from investing:
- Evidence-based investing calls for estimating an asset’s expected return, based on these kinds of informed fundamentals.
- Evidence-based investing also calls for us to factor in how different asset classes interact with one another. This helps us fit each piece into a unified portfolio that we can manage according to individual goals and risk tolerances.
- Evidence-based investing calls for a long-term, buy, hold and rebalance strategy.
Cryptocurrency simply doesn’t yet synch well with these parameters. It does have a price, but it can’t be effectively valued for planning purposes, especially amidst the extreme price swings we’re seeing of late.
What if I decide to buy some cryptocurrency anyway?
We get it. Even if it’s far more of a speculative than investment endeavor, you may still decide to give cryptocurrency a go, for fun or potential profit. If you do, here are some tips to consider:
- Think of it as being on par with an entertaining trip to the casino. Nothing ventured, nothing gained – but don’t venture any more than you can readily afford to lose!
- Use only “fun money,” outside the investments you’re managing to fund your ongoing lifestyle.
- Educate yourself first, and try to pick a reputable platform from which to play. (CoinDesk offers a pretty good bitcoin primer.)
- If you do strike it rich, regularly remove a good chunk of the gains off the table to invest in your managed portfolio. That way, if the bubble bursts, you won’t lose everything you’ve “won.” (Also set aside enough to pay any taxes that may be incurred.)
Last but not least, good luck. Whether you win or lose a little or a lot with cryptocurrency – or you choose to only watch it from afar for now – we remain available to assist with your total wealth, come what may.








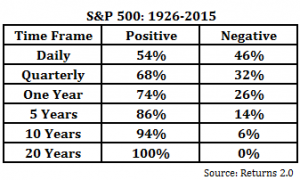 2) Capital markets have exhibited an upward trajectory over the long-term, yielding positive, inflation-beating returns to those who have stayed put for the ride.
2) Capital markets have exhibited an upward trajectory over the long-term, yielding positive, inflation-beating returns to those who have stayed put for the ride.